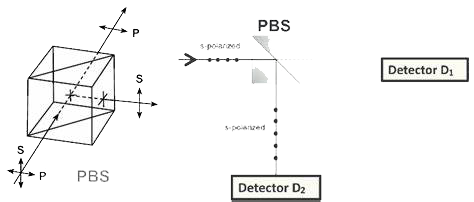
The beamsplitter is an optical component that divides an incident beam into two beams propagating in mutually perpendicular directions. Unlike general optical splitting elements, the two beams produced by it have a unique relationship: both beams are linearly polarized, and their polarization directions are perpendicular to each other.
The composition of a polarizing beam splitter: It is typically made by cementing or optically contacting the hypotenuse sides of two right-angle prisms, with a polarizing beam splitting film applied to the hypotenuse. P-polarized light in the incident light is transmitted, while S-polarized light is reflected. Anti-reflective coatings are generally applied to all the incident and exit surfaces of the light beams.
The polarizing beam splitter divides incident light into two orthogonally polarized components:
Transmitted light (T): p-polarized
Reflected light (R): s-polarized
Working Mechanism:
When light enters the right-angle prism perpendicularly through its hypotenuse face, the embedded multilayer coating induces Brewster's angle refraction at dielectric interfaces
Through optimized thin-film design:
p-polarized light experiences near-zero reflection loss (transmittance >90%) due to Brewster angle conditions
s-polarized light undergoes cumulative reflections across multiple coating layers, achieving >99.5% reflectance
Incident Light Requirements:
No polarization restriction: Both natural light and pre-polarized light can be effectively split into orthogonal components
| Transmitted (T) | Reflected (R) | |
| Polarization | p-polarized | s-polarized |
| Extinction Ratio | TP/TS >1000:1 | RS/RP >1000 |
| Beam | <±5 arcmin | 90°±5 arcmin |
| Material | Optical glass |
| Diemsinon tolerance | ±0.2 |
| Surface flatness | λ/4@632.8nm |
| Surface quality | 60/40 or better |
| Clear aperture | >90%外形尺寸 |
| Extinction Ratio: | Tp/ Ts>2000:1 |
| Output beam deviation: | 0°±3'(T),90°±5'(Rs) |
| Incidence angle: | 0°~2° |
| Coating: | Functional layer: Polarization beam-splitting coating deposited on hypotenuse surface (Ta₂O₅/SiO₂ multilayer stack) Anti-reflective treatment: Narrowband multilayer anti-reflective coating (R<0.25%) applied to all four external surfaces |
| Temperature range: | -30℃ to +70℃ |
| Type No. | Wavelength | Dimension | Extinction Ratio |
| AT-PBS-12.7@532 | 532nm | 12.7×12.7×12.7 | Tp/ Ts>2000:1 |
| AT-PBS-25.4@532 | 532nm | 25.4×25.4×25.4 | Tp/ Ts>2000:1 |
| AT-PBS-12.7@633 | 633nm | 12.7×12.7×12.7 | Tp/ Ts>2000:1 |
| AT-PBS-25.4@633 | 633nm | 25.4×25.4×25.4 | Tp/ Ts>2000:1 |
| AT-PBS-12.7@1064 | 1064nm | 12.7×12.7×12.7 | Tp/ Ts>2000:1 |
| AT-PBS-25.4@1064 | 1064nm | 25.4×25.4×25.4 | Tp/ Ts>2000:1 |
1. Multiphoton Imaging
Optical Isolation: PBS combined with a quarter-wave plate (QWP) creates optical isolators to control light propagation paths. This setup converts linearly polarized light to circularly polarized light, preventing back-reflections from disrupting the imaging system.
Intensity Modulation: By integrating PBS with a half-wave plate (HWP), rotating the HWP adjusts the polarization angle of incident light, enabling precise control of light intensity and power output.
2. Laser Interferometry
Beam Splitting and Interference: In Michelson interferometers, PBS splits laser light into two orthogonal polarized beams (P and S). One beam reflects off a fixed mirror, while the other reflects off a moving mirror. The recombination of these beams produces interference patterns with a 90° phase shift, allowing precise measurement of displacement via photodetectors.
Heterodyne Interferometry: PBS separates dual-frequency laser beams for applications requiring Doppler-shift detection, enhancing measurement accuracy in aerospace and precision manufacturing.
3. Optical Instrumentation
Error Correction in CNC Machines: PBS-based interferometers are critical for calibrating CNC machines, ensuring micron-level precision by detecting mechanical deviations.
3D Imaging: In stereoscopic displays, PBS separates orthogonal P/S polarized light for left/right eye channels, enabling immersive 3D effects when paired with polarized glasses.
4. Broadband and Narrowband Applications
Broadband PBS (420–1600 nm): Suitable for systems requiring wide spectral coverage, such as fluorescence microscopy and tunable lasers. These PBS maintain high extinction ratios (>1000:1) and low absorption losses across broad wavelengths.
Narrowband PBS: Optimized for specific wavelengths (e.g., 632.8 nm or 1700 nm), these components are used in waveplates and fiber-optic systems to convert linear to circular polarization via birefringent crystals (e.g., quartz or calcite).
If you would like to build your own precision optical products or request a quote, please click one of the two buttons below. Otherwise, please fill out the form below with any questions or concerns.

Address
B3 Shengshi Shengshi Industrial Park,Auto-ETDZ, Changchun, Jilin, China
Call Us